What is Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is a condition that occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) causes inflammation in a superficial vein. It usually affects veins in the legs and can cause pain, swelling, and redness. The term “superficial phlebitis” is often used as a preliminary diagnosis until further tests are done to confirm the presence of a clot. This term refers to inflammation and pain in the vein without a confirmed blood clot.
If you experience symptoms of thrombophlebitis, it is important to see a doctor immediately to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment for thrombophlebitis may include medication, compression stockings, or in some cases, blood thinning medication. Your doctor can help determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
There are three specific kinds of thrombophlebitis, diagnosed by location:
- Superficial thrombophlebitis (STP)
- Superficial Venous Thrombosis (SVT)
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
What are the symptoms of Thrombophlebitis?
Several symptoms may accompany thrombophlebitis, including:
- SWELLING – Recent swelling of the limb.
- PAIN – Unexplained limb pain or tenderness.
- WARMTH – Skin that may be warm to the touch.
- REDNESS — Redness of the skin.
If a vein near the surface of your skin is affected, you may notice a red, firm cord just under the surface of your skin that can be painful when touched. When a deep vein in your leg is affected, you may experience swelling, tenderness, and pain, making walking difficult. It’s important to seek medical attention if you notice any of these symptoms, as they may indicate a serious condition that requires prompt treatment. Call 911 if you have any symptoms of shortness of breath, knife-like chest pain on inspiration, coughing up blood, or rapid heartbeat.
What are the risk factors of Thrombophlebitis?
Risk factors for developing thrombophlebitis include:
- Oral contraceptives and birth control
- Prolonged periods of sitting or standing
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Certain medical conditions
- Advanced age
- Certain genetic states. (Factor V Leiden)
- Hormonal Therapy. (Estrogen)
- Recent surgery/trauma
- Malignancy/Active cancer
- Pre-existing venous disease/varicose veins
- Pregnancy
Thrombophlebitis Treatment Overview
To properly diagnose thrombophlebitis, we may order additional lab work and imaging tests, such as ultrasonography, to better visualize the affected vein. This is done in conjunction with a thorough history-taking and physical examination to determine the extent and severity of the condition. To alleviate symptoms, treatment options for superficial thrombophlebitis may include anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs and compression stockings. However, if the thrombophlebitis is affecting a deep vein or there is evidence of it encroaching on the deep venous system, anticoagulation medication (blood thinner) may be necessary to prevent the formation or worsening of a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). We will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your individual situation and medical history.
The Region Vein Approach
At Region Vein, we take the impact of thromboembolic disease on our patients and their families seriously. We recognize that underlying venous disease can be a significant factor for many patients affected by thrombophlebitis. That’s why we work closely with your referring physician to create a customized care plan that meets your specific needs. By collaborating with your doctor, we can ensure you receive the best possible care and treatment for your condition.
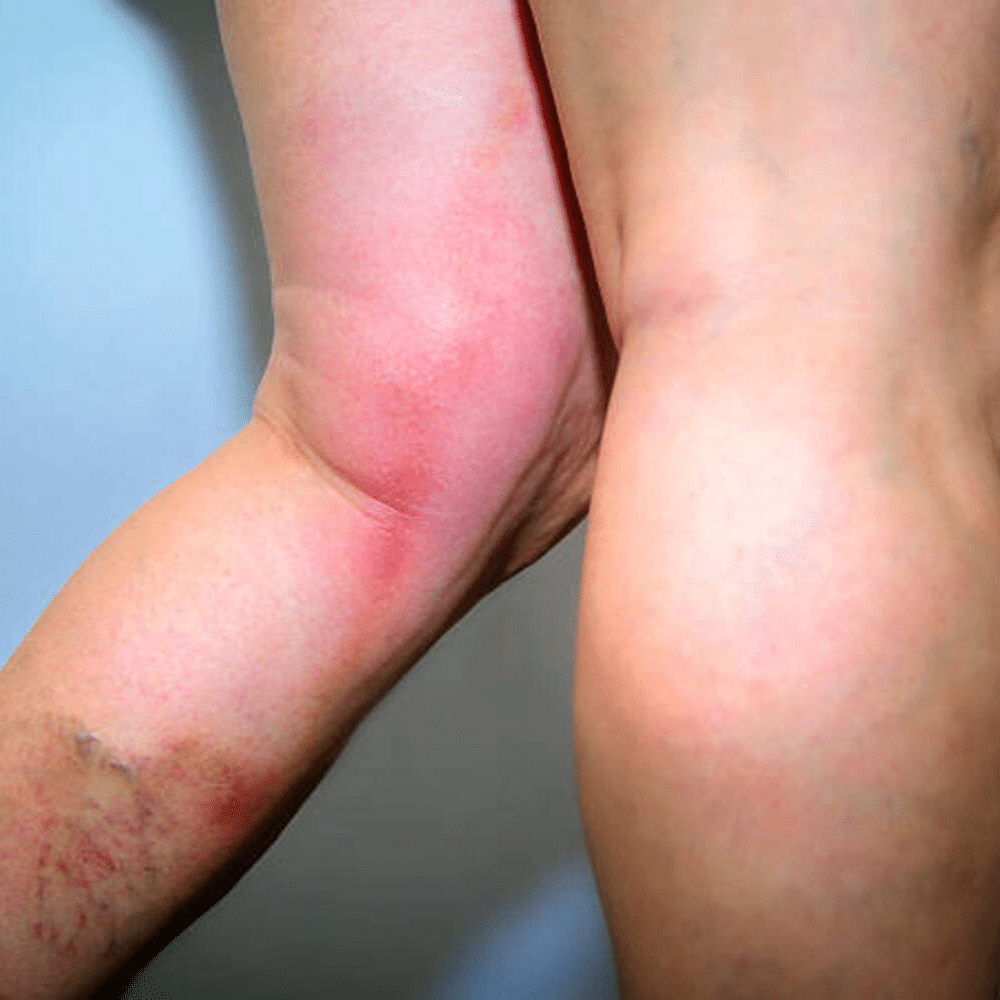
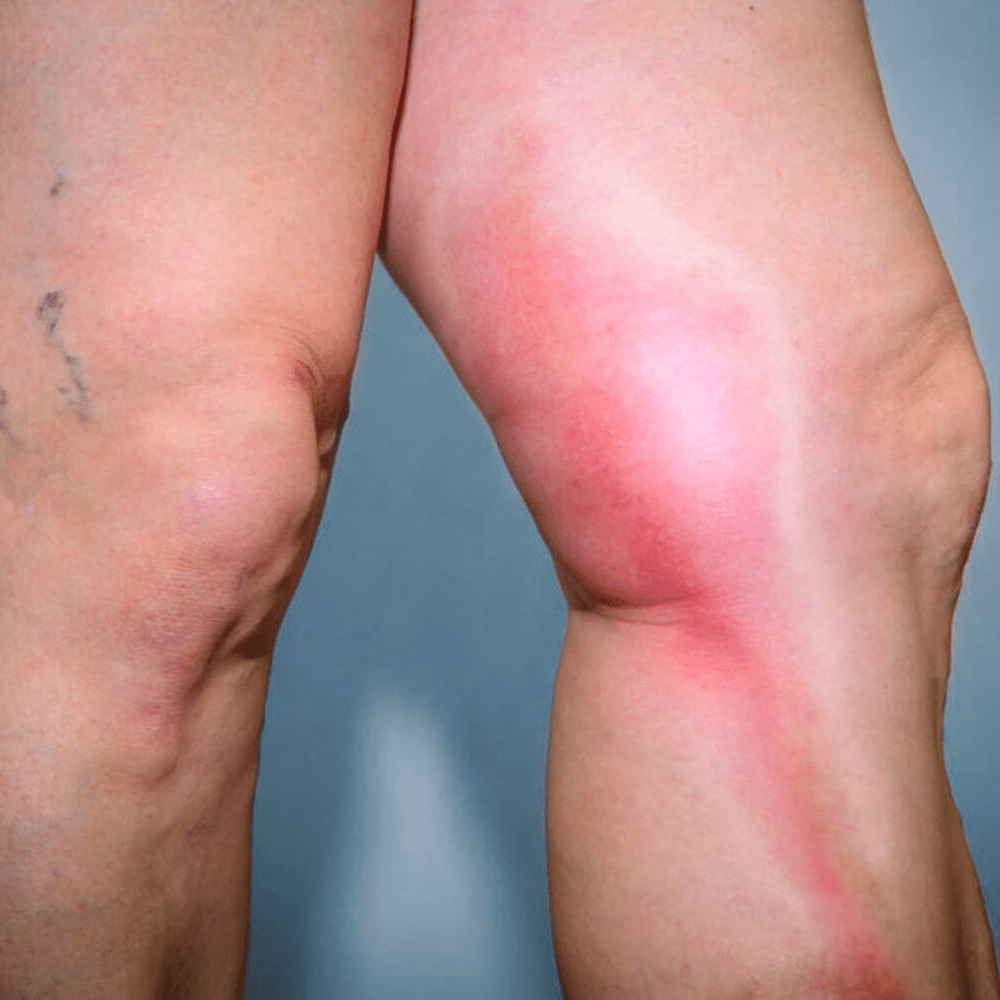
More About Thrombophlebitis
Superficial Thrombophlebitis (STP) typically affects veins in the skin’s surface layers, particularly in the legs. These veins are often large caliber and dilated varicose veins. Superficial Venous Thrombosis (SVT) occurs when a thrombus is found in larger superficial saphenous veins, such as the great saphenous vein. Depending on the location of the SVT, it may extend or propagate into the deep venous system, which can result in a more severe condition known as deep venous thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when a thrombus forms in the deep veins of the legs, deep in the muscle layer. If left untreated, there is a risk that the clot may break off and travel to the lungs, leading to a potentially life-threatening complication known as pulmonary embolus (PE).
It is important to note that underlying venous disease can contribute to the development of STP and SVT, so it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. At Region Vein, we take thromboembolic disease seriously and work closely with referring physicians to determine the best course of treatment for each patient.